Sheet metal is an indispensable material in various industries, including construction, automotive, and aerospace. Its versatility and ability to be easily molded into various shapes and sizes have made it a favorite among engineers and manufacturers alike. However, choosing the right thickness or gauge of sheet metal is crucial for ensuring that the final product meets the desired standards. This is where a sheet metal gauge chart comes in handy. In this post, we will take a closer look at sheet metal gauge charts and how they are used in the industry.
What is a sheet metal gauge chart?
A sheet metal gauge chart is a simple tool used to determine the thickness or gauge of sheet metal. The chart lists different thicknesses in both inches and millimeters, along with their corresponding gauge numbers. The gauge numbers, ranging from 0 to 36, represent the thickness of the metal sheet. The higher the number, the thinner the sheet metal.
 A sheet metal gauge chart is essential for determining the appropriate thickness of sheet metal for the intended use. For instance, if you are using sheet metal for roofing, you need to choose a thicker gauge, while thinner gauges are ideal for making ductwork or decorative objects.
A sheet metal gauge chart is essential for determining the appropriate thickness of sheet metal for the intended use. For instance, if you are using sheet metal for roofing, you need to choose a thicker gauge, while thinner gauges are ideal for making ductwork or decorative objects.
How is a sheet metal gauge chart used?
Using a sheet metal gauge chart is simple. First, you need to identify the application or project you intend to use the sheet metal for. Then, check the chart to find the recommended thickness or gauge number for that particular application. Once you have identified the gauge number, you can proceed to select the appropriate sheet metal thickness.
It is worth noting that sheet metal gauge charts are merely guidelines. The actual thickness of the sheet metal may vary slightly depending on the material used, the manufacturing process, and other factors. As such, it is always advisable to consult with a sheet metal expert or manufacturer when in doubt about the appropriate gauge number for your project.
 Understanding sheet metal gauge numbers
Understanding sheet metal gauge numbers
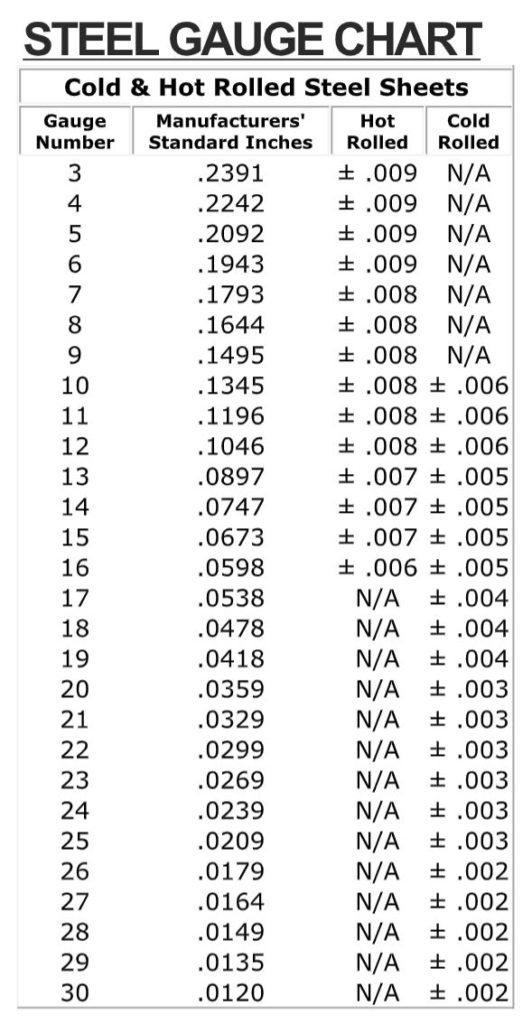
Sheet metal gauge numbers are used to indicate the thickness of sheet metal. The higher the gauge number, the thinner the sheet metal. For instance, a gauge number of 30 indicates a thickness of 0.012 inches, while a gauge number of 20 represents a thickness of 0.0359 inches.
It is essential to note that not all sheet metal materials have the same thickness for the same gauge numbers. This is because the thickness of sheet metal varies depending on the type of material used. For example, a gauge number of 16 steel sheet metal has a thickness of 0.0598 inches, while a gauge number of 16 aluminum sheet metal is 0.0508 inches.
 Choosing the right gauge number for your project
Choosing the right gauge number for your project
Choosing the right gauge number for your project is crucial to ensure a successful outcome. Factors such as the intended use of the sheet metal, the level of strength required, and the manufacturing process used will determine the appropriate gauge number. Here are some of the most common sheet metal gauge numbers and their recommended uses:
- Gauge number 22 – Ideal for light-duty projects such as lampshades and small jewelry boxes
- Gauge number 20 – Suitable for making ductwork, appliance panels, and highway signs
- Gauge number 18 – Recommended for roofing, gutter systems, and boat hulls
- Gauge number 16 – Suitable for chassis fabrication, truck beds, and metal furniture
- Gauge number 14 – Recommended for heavy-duty projects such as electrical enclosures and large HVAC systems
- Gauge number 12 – Ideal for industrial roofing, building facades, and large tanks
- Gauge number 10 – Recommended for heavy-duty projects such as industrial sheds and storage facilities
Sheet metal gauge chart vs. thickness gauge chart: what is the difference?
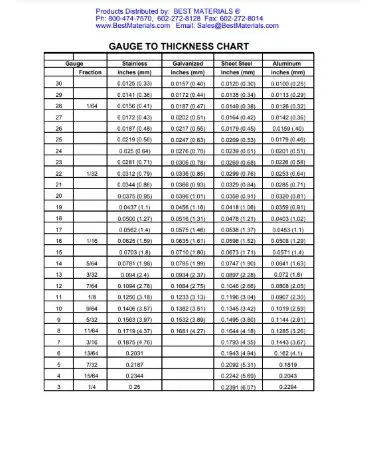
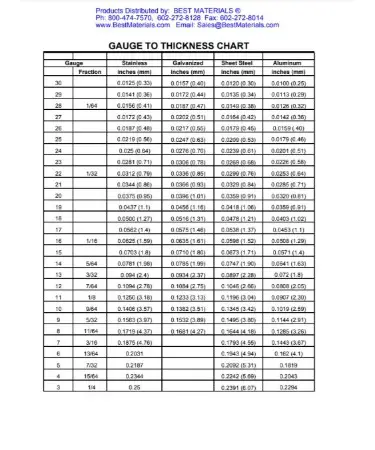
While sheet metal gauge charts are used to determine the thickness of sheet metal, a thickness gauge chart is used to measure the thickness of the material. Thickness gauge charts list the thickness of various materials in both inches and millimeters. The charts are used to ensure that the actual thickness of the material matches the intended thickness.
 Thickness gauge charts are commonly used in the manufacturing of plastic and rubber products, while sheet metal gauge charts are mainly used in the fabrication of sheet metal products. Both types of charts are essential in ensuring that the final product meets the intended specifications.
Thickness gauge charts are commonly used in the manufacturing of plastic and rubber products, while sheet metal gauge charts are mainly used in the fabrication of sheet metal products. Both types of charts are essential in ensuring that the final product meets the intended specifications.
Advantages of using a sheet metal gauge chart
Using a sheet metal gauge chart comes with several advantages, including:
- Accurate determination of the appropriate gauge number for the intended use
- Time-saving, as it eliminates the need for trial and error when selecting the appropriate gauge number
- Cost-saving, as it reduces the chances of choosing the wrong gauge number, which can result in wasted resources and money
- Better quality products, as the appropriate gauge number ensures that the final product meets the intended strength and durability standards
 Factors to consider when choosing a sheet metal gauge chart
Factors to consider when choosing a sheet metal gauge chart
When choosing the appropriate sheet metal gauge chart, there are several factors to consider. These include the intended use of the sheet metal, the manufacturing process used, the properties of the material used, and the level of strength required. It is also important to consider the expertise of the manufacturer or supplier of the sheet metal, as they can provide valuable insights into the appropriate gauge number for your project.
 Common misconceptions about sheet metal gauge charts
Common misconceptions about sheet metal gauge charts
There are many misconceptions about sheet metal gauge charts. Here are some of the most common misconceptions:
- All sheet metal with the same gauge number has the same thickness: This is not true, as sheet metal thickness varies depending on the type of material used.
- Sheet metal gauge charts are the only factor to consider when selecting the appropriate gauge number: While sheet metal gauge charts are crucial in selecting the appropriate gauge number, other factors such as the manufacturing process used, and the level of strength required should also be considered.
- All sheet metal gauge charts are the same: Sheet metal gauge charts vary depending on the manufacturer or supplier and the intended use. It is essential to select the appropriate sheet metal gauge chart for your specific application.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a sheet metal gauge chart is a valuable tool used in the selection of the appropriate sheet metal thickness for various applications. It lists the thickness of different sheet metal gauges in both inches and millimeters, making it easy to determine the appropriate gauge number for the intended use. However, sheet metal gauge charts are just guidelines, and it is advisable to consult with a sheet metal expert or manufacturer when in doubt about the appropriate gauge number for your project. By choosing the appropriate gauge number, you can ensure that your final product meets the desired standards of strength and durability.
 Choosing the right gauge number for your project is crucial to ensuring a successful outcome. It is also essential to consider other factors such as the manufacturing process used, the level of strength required, and the expertise of the manufacturer or supplier of the sheet metal. By considering these factors, you can select the appropriate sheet metal gauge chart and gauge number to meet the desired specifications. Ultimately, using a sheet metal gauge chart can save time and money, and give you peace of mind knowing that your final product meets the intended standards.
Choosing the right gauge number for your project is crucial to ensuring a successful outcome. It is also essential to consider other factors such as the manufacturing process used, the level of strength required, and the expertise of the manufacturer or supplier of the sheet metal. By considering these factors, you can select the appropriate sheet metal gauge chart and gauge number to meet the desired specifications. Ultimately, using a sheet metal gauge chart can save time and money, and give you peace of mind knowing that your final product meets the intended standards.