As an expert in electrical matters, I am pleased to provide some insights on ohms law which is an important concept in the field. This law describes the relationship between current, resistance, and voltage in a circuit, and knowing how to calculate these variables is crucial for any electrician or inspector.
Understanding Ohms Law
 At its core, Ohm’s Law states that the current in a circuit is directly proportional to the voltage across the circuit and inversely proportional to the resistance of the circuit. In other words, as the voltage increases, the current increases, and as the resistance increases, the current decreases. This relationship can be expressed mathematically using the equation:
At its core, Ohm’s Law states that the current in a circuit is directly proportional to the voltage across the circuit and inversely proportional to the resistance of the circuit. In other words, as the voltage increases, the current increases, and as the resistance increases, the current decreases. This relationship can be expressed mathematically using the equation:
I = V/R
where I is the current in amperes (A), V is the voltage in volts (V), and R is the resistance in ohms (Ω). This equation can be rearranged to solve for any of the three variables. For example:
V = I * R
R = V / I
Applying Ohms Law
 Understanding Ohm’s Law is essential for analyzing and troubleshooting electrical circuits. For example, consider a circuit with a 12-volt battery and a total resistance of 3 ohms. We can use Ohm’s Law to calculate the current in the circuit:
Understanding Ohm’s Law is essential for analyzing and troubleshooting electrical circuits. For example, consider a circuit with a 12-volt battery and a total resistance of 3 ohms. We can use Ohm’s Law to calculate the current in the circuit:
I = V / R = 12 V / 3 Ω = 4 A
With this information, we can also calculate the power dissipated in the circuit using the formula:
P = I * V = 4 A * 12 V = 48 W
Knowing the power dissipated can help determine if the components in the circuit are rated for the appropriate voltage and current.
Additional Tools for Electrical Calculations
 While understanding Ohm’s Law is essential, there are additional tools and formulas that can be used for electrical calculations. For example, the power dissipated in a circuit can also be calculated using the formula:
While understanding Ohm’s Law is essential, there are additional tools and formulas that can be used for electrical calculations. For example, the power dissipated in a circuit can also be calculated using the formula:
P = V^2 / R = I^2 * R
where ^2 denotes squaring. Similar to how Ohm’s Law can be rearranged to solve for different variables, this formula can also be rearranged to solve for voltage or resistance.
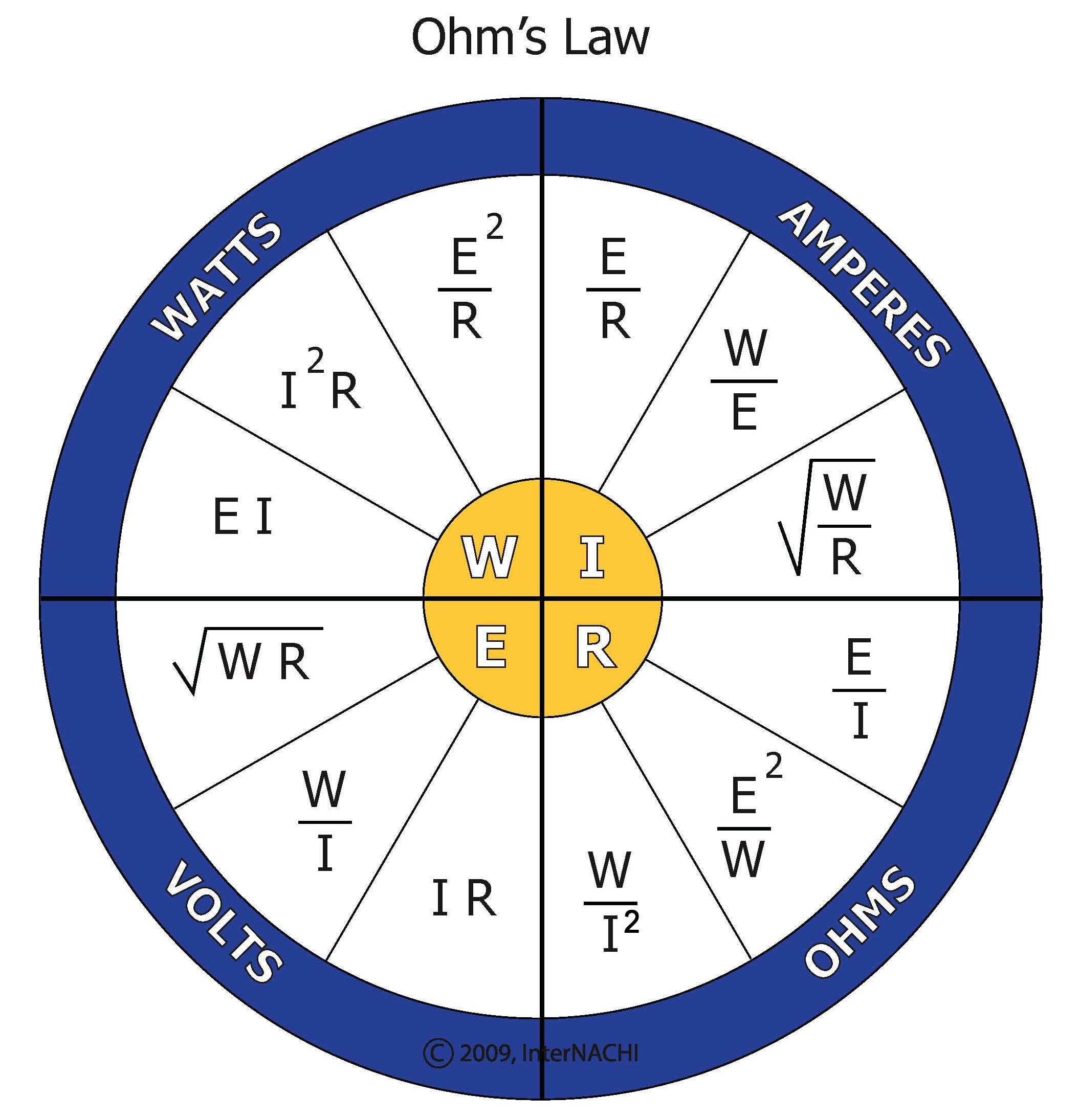
Another useful tool is the Ohm’s Law Power Wheel, shown above. This wheel can be used to quickly and easily calculate different electrical values, such as power and resistance, by simply spinning the wheel to align the appropriate variables. This tool can be especially useful for troubleshooting circuits in the field.
Conclusion
Overall, Ohm’s Law is a fundamental concept in electrical circuits and an essential skill for anyone in the field. By understanding the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance, electricians and inspectors can troubleshoot, analyze, and design circuits with confidence. There are also additional tools and formulas that can be used for more complex calculations, such as the power dissipated in a circuit. With these tools and a comprehensive understanding of Ohm’s Law, anyone can excel in the field of electrical engineering and inspection.